Matrices and lines of transmission
Matriciale Representation of nets 2 doors
1) Matrices for the representation of nets 2 doors:
to) Matrix of the stiffnesses
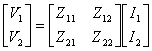
b) Matrix of the admittances
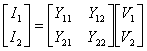
c) Matrix of transmission
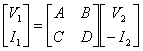
The most used the matrix of total transmission is the matrix of transmission in how much for nets 2 doors in cascade is simply the product of the single matrices of transmission.
2) Relation between the coefficients of the Z matrix and the coefficients of the transmission matrix:
It is necessary to write ![]() the in terms
of V2 and of I2 to such aim from
the in terms
of V2 and of I2 to such aim from ![]() the
the
![]() is gained and it is replaced,
is gained and it is replaced, 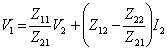 is obtained therefore has
is obtained therefore has ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
In analogous way the values of and ![]() in
in ![]() function of the parameters are obtained z.
function of the parameters are obtained z.
3) Condition of reciprocity and symmetry for the transmission matrix:
The symmetry of the net is guaranteed in the case has A=D while the reciprocity is had in the case has AB-CD=1.
4) Stiffness of a log of line finished on ZL :
![]() being
being ![]() the electric length of the line
the electric length of the line
5) Matrix ABCD for one transmission line:
The Z matrix is estimated before leaving from the ![]() formula and then taking advantage of the relation
between the coefficients of the Z matrix and the coefficients of the
transmission matrix it is reached this last one, is had:
formula and then taking advantage of the relation
between the coefficients of the Z matrix and the coefficients of the
transmission matrix it is reached this last one, is had:
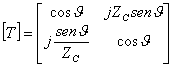
6) Adapter to l/4:
In the case the cargo has a various stiffness from that
one of the line is had of the reflections, in order to adapt can be
used a transformer to l/4 that is
substantially a feature of having line alongl /4 that is electric length J = p/2, its
characteristic stiffness must be such that sluice on ZL present in income the characteristic
stiffness of the line to adapt that is 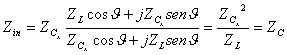 from
cui
from
cui ![]() .
.
7) Matrix of scattering:
We consider a net n-doors and we close i-1 doors on a
cargo stiffness Z0 so as to to
adapt them, i-esima the door instead comes sluice on a generator of
tension V with inner stiffness Z0, in circuit it will be characterized
from a direct wave ![]() and a reflected wave
and a reflected wave ![]() tied from the reflection coefficient.
tied from the reflection coefficient.
In particular for a net 2-doors the matrix of scattering
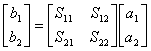 is had that in the case of a mutual net
introduces S21 = S12 if the net is also symmetrical then S11 = S22 and in absence of losses instead
is had that in the case of a mutual net
introduces S21 = S12 if the net is also symmetrical then S11 = S22 and in absence of losses instead 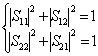 .
.
8) Relation between the matrix of scattering and matrix ABCD:
The transmission matrix gives an expression to us is for V1 that for I1 , replacing them with to the condition
of ![]() closing in
closing in ![]() the is
obtained
the is
obtained 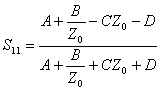 .
.
In analogous way 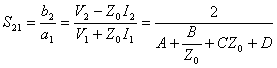 like pure
like pure 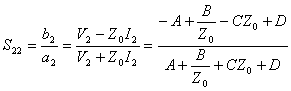 is obtained while S12 does not come calculated in how much in all the circuits
analyzes to you will have S21
= S12 .
is obtained while S12 does not come calculated in how much in all the circuits
analyzes to you will have S21
= S12 .
Lines of transmission
9) Stripline:
The Stripline is constituted from a conductor dipped in a
dielectric having constant andr enclosed between one advanced metalization and one
inferior metalization. Be a matter itself of a homogenous
structure a fundamental way TEM with constant of phase
concurs ![]() . It comes above all used and to vlves
little.
. It comes above all used and to vlves
little.
10) Microstriscia:
A mass plan is constituted from a high dielectric h with
below and overhanging a metallic strip high t and wide W, concurs the
propagation of a fundamental way âquasi-TEMâ? with frequency of
cut-off null in how much is 2 conductors and two dielectrics therefore
pu² propagare also the continuous one. One cannot be defined
constant dielectric for the structure in how much is 2 dielectrics,
the air and the substrate, therefore it comes defined one constant
effective dielectric 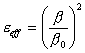 which is greater of andr ,
value that ideally assumes when W®¥ and therefore all the lines of
force are contained in the substrate, and minor of
which is greater of andr ,
value that ideally assumes when W®¥ and therefore all the lines of
force are contained in the substrate, and minor of ![]() , value that assumes in the case W®0 and therefore the lines of
force pass for half in the substrate and half in air. More the
microstrip is tightened more increases the stiffness characteristic.
, value that assumes in the case W®0 and therefore the lines of
force pass for half in the substrate and half in air. More the
microstrip is tightened more increases the stiffness characteristic.
11) Model to magnetic walls for the microstrip:
The microstrip to analyze is equivalent to a high
dielectric h that it is comprised between two wide metallic sheets WEFF to the edges di.le which are
two magnetic walls, in particular has 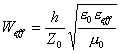 > W in how
much is necessary to hold account also of the fringing field.
> W in how
much is necessary to hold account also of the fringing field.
12) Coplanare:
It is constituted from a dielectric substrate over to which a metalization is had centers them wide 2a and 2 plans of mass separate you from a distance 2b, in order to maintain them the same one it upgrades them are necessary of the ponticellature however in order to place a point to mass is not necessary via-hole as instead it happens for the microstrip. Values of characteristic stiffness between 20 can be obtained150 W andW against the 120W of the microstrip this because the elevated characteristic stiffnesses obtain the how many the more lines of force pass in air.
13) Lines of transmission on membrane:
The substrate is constituted from a thick membrane approximately 1mm, it derives some that not due and and EFF @ 1 arelosses toit, its advantages regarding the other types of lines to microwaves is obvious beyond the 30GHz.
14) Comparison between hybrid and monolitici integrated circuits:
In the hybrids the alumina is used like substrate, the active elements comes glue to you on it and connects to you between they through threads, this concurs to carry out the tuning of the circuit, what that is not possible with the monolitici circuits where elements assets and liabilities to you share the same substrate semiconductor. To observe that for the monolitici it is preferred to use the elements it concentrates to you rather than the lines in how much they introduce dimensions many not compatible elevating with the necessities to miniaturize inborn in the plan of the monolitici circuits.
15) Discontinuity on microstrip:
with) the step it concurs to pass from a stiffness Z1 to a stiffness Z2 that evidently is greater in the case that W2 < W1, is is step symmetrical that asymmetric.
b) splices are to T that to cross
c) gap capacitivo obtained simply with a carving in the microstrip
d) bend draft of curvings that come dulled to the aim to avoid the reflections
16) Stub for microstrip:
The stub opened he is simpler to realize regarding the stub in short that it demands via-hole, are opened problems with the stub with low characteristic stiffness, they are in fact much wide, a lot that the insertion point more very is not defined and can risuonare laterally, have been develops to you therefore of the stub radial
17) Discontinuity in coplanare:
They are conceptually identical to the discontinuities for microstrip, the only important difference is that still they have not been develops you of the reliable models for the discontinuities in complanare.
18) Inductances to microwaves:
The following realizations are possible:
to) line to meandro
b) line to S
c) line to spiral
the last configuration is used even if demands than a bridge in order to capture it marks them from the center of the spiral.
It is possible also to realize an inductance by means of a
line of short transmission and to high characteristic stiffness in
fact confronting the two matrices of transmission ![]() e
e 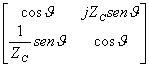 it is obvious that
for small J and largeZ C the two matrices
correspond and
it is obvious that
for small J and largeZ C the two matrices
correspond and ![]() .
.
19) Ability to microwaves:
The following realizations are possible:
to) gap capacitivo with values of ability comprised between 0.001pF and 0.05pF
b) Ability interdigitata with values comprised between 0.01pF and 0.5pF
c) Abilities MIM with values comprised between 0.1pF and 100pF pu² being realized are with a single level of metalization that with two levels.